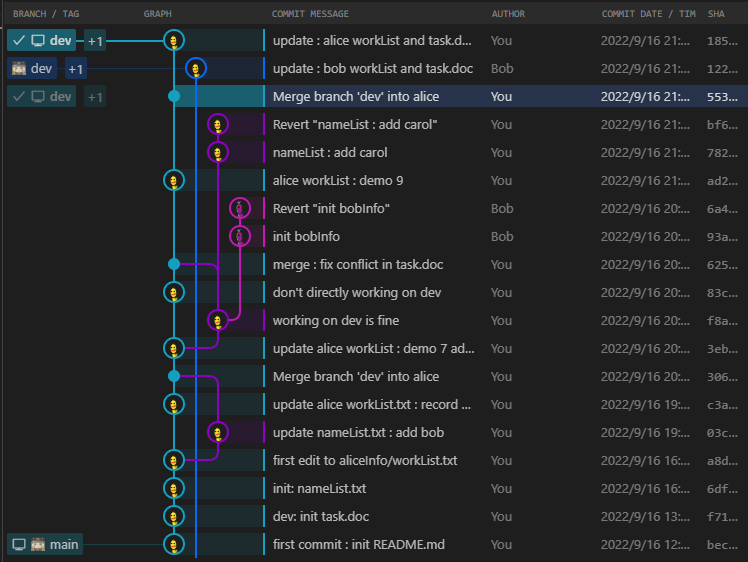
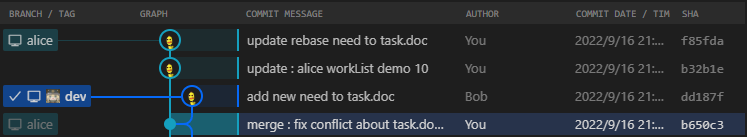
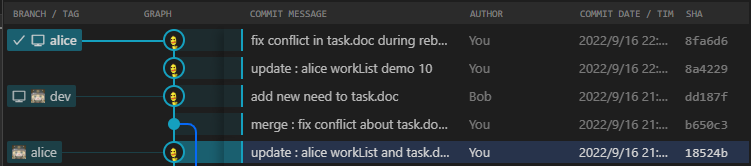
git原理
git意义
1.作用
版本控制功能:在本地端记录文件的修改记录,在远程仓库备份内容和版本记录
协同开发控制:保证多人同时开发时,开发内容不会冲突
2.远程仓库的选择
可以选择github gitee等远程仓库储存自己的代码
也可以使用gitlab在本地搭建代码库
git原理
参考: 这才是真正的Git——Git内部原理揭秘! - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
可视化工具: Explain Git with D3 (onlywei.github.io)
1.git项目
对于git管理的项目主要分为两个部分,工作区和git仓库区:
- 工作区指项目开发的所有文件所在的区域
- git仓库区则是项目根目录下./.git目录的内容,其中主要记录了git需要的相关信息
git主要使用SHA1散列算法将工作区的各文件内容、拓扑信息、修改记录转为git对象储存在git仓库中。而利用散列算法是为了快速比对文件是否相同。
2.git对象
参考: Git(Linux环境):Git对象模型(blob、tree、commit、tag)_NGC_2070的博客-CSDN博客
git会对每个加入git仓库(即经过git add后)的文件创建对应的git对象,并且通过散列哈希算法保证文件内容不同时生成的git对象对象名也不同,因此只要文件发生改动,就会生成新的对应git对象
1 | # 底层指令 |
2.1 git对象类型
一共有4种数据对象:blob,tree,commit,tag. 他们都被储存于./.git/objects目录中,如下:
1 | ### 检视git对象 ### |
2.1.1 blob对象
存储工作区中被git add指令添加过的具体文件
而一个文件经过多次修改后,每git add 一次,就会在仓库内产生一个新的blob对象。因此 blob 文件就是对原文件内容的全量拷贝,同时前面加了 blob size\0,而文件名称的 hash 值计算是计算整体字符的 SHA-1 值

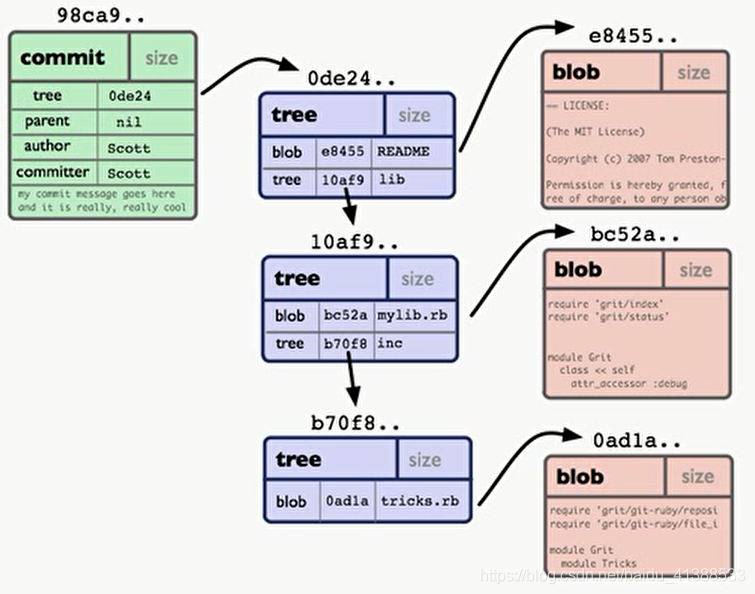
2.1.2 tree对象
储存一串指向其他blob或tree对象的指针,用于表示目录与内容的层次关系
且由于tree指向的也是git对象类型,那么当tree指向工作区同一个文件的
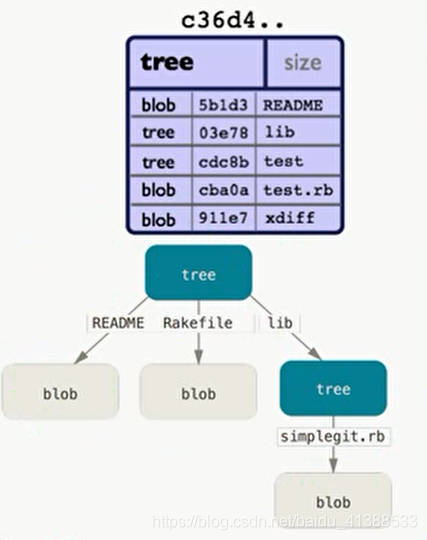
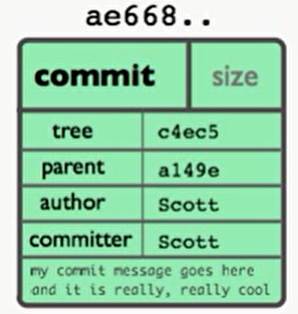
2.1.3 commit对象
commit用来指向一个tree对象,标记项目某个特定时间点状态,记录commit时提交的对应信息
指向的tree对象,将指向本次提交对应的所有object, 因此可以认为每个commit就是整个项目的一个快照
2.1.4 tag对象
用来标记某一个提交(commit)
2.2 对象命名规则
用40个字符的字符串用来表示对象名:目录(2个字符)+名(38个字符)
字符串由对象内容做SHA-1哈希计算得来
2.3 查看git对象
因为git对象都是二进制加密后的,因此直接使用cat读取是无法正常读取内容的
git cat-file -t <文件名> 查看git对象类型
git cat-file -p <文件名> 查看git对象内容
1 | ### blob类型 ### |
3.工作区与暂存区
git将项目划分为工作区、暂存区、本地仓库、远程仓库四部分
工作区:就是实际操作并改动的文件。在VsCode插件中,工作区的文件有以下几种状态:
- U: untracked, 表示文件刚创建,但是没有通过
git add提交到工作区,自然也没有其对应的blob对象对其进行备份 - M modify, 表示文件发生过,但是没有通过
git add提交到工作区,与其之前的blob对象不匹配 - A tracked, 文件在改动后以及提交到了暂存区,这个文件以及有了对应的blob对象储存其备份信息,在
git status中会提示”need to commited”。但是一旦该文件再次发生改动,就会回到untracked状态 - ! conflict, 表示该文件发生冲突,同时被多个分支修改
- 其他: 相比当前HEAD指向的快照没有发生变动的文件,在
git status中不会提示相关信息
暂存区:指进行过改动,但是没有添加对应的git对象至本地仓库的文件区域,记录于./.git/index文件中
本地仓库:指./.git中储存的各种指针、git对象、提交记录等信息,可以视作工程的快照与文件的修改记录信息,可以用于回滚版本
远程仓库:例如github gitee gitlab等远程用来备份项目的仓库
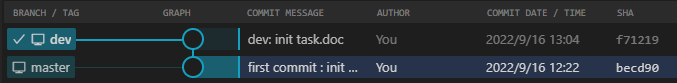
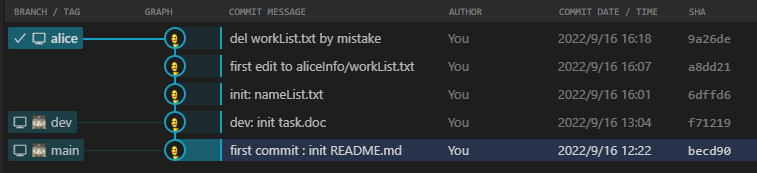
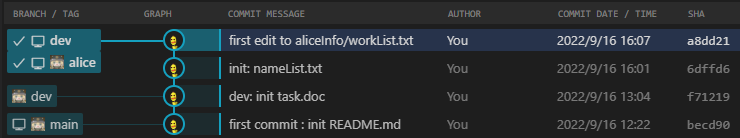
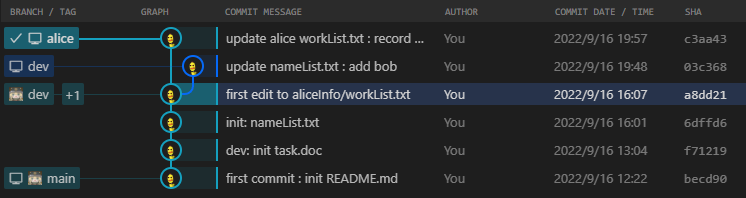
4.git分支与git指针
每个git分支都有一个指针,他会指向当前分支的最新快照,也就是指向最新commit提交给当前分支的那个commit对象。其中,各分支的指针储存在./.git/refs/heads/<分支名>中;而各分支指针指针的改动历史则储存在./.git/logs/refs/heads/<分支名>中
1 | # 分支对应指针 |
除了git分支的指针外,还有HEAD指针,HEAD指针永远指向最近一次commit提交对应的commit对象。HEAD指针存储在./.git/HEAD中,HEAD指针的历史记录储存在./.git/logs/HEAD中
1 | # HEAD指针内容 |
5.git的垃圾回收gc
经过多次的commit后,git对象中可能有多个blob或tree类型已经是指针不可达的状态,这时候git gc命令可以用于回收这些不可用的git对象
如果存储库中的松散对象太多或包装太多,则需要进行内务处理。如果松散对象的数量超过了gc.auto配置变量的值,则所有松散对象都将使用组合到一个包中git repack -d -l
1 | # 清理不必要的文件并优化本地存储库 |